Tutorial Draw The Circuit Diagram Used To Assert Ohm's Discharge Duty For Free
16+ Info draw the circuit diagram used to assert ohm's discharge duty for Free
Draw a circuit diagram to measure experimental set going on for encouragement of
16 Apr 2020 The experimental circuit diagram to assert the ohm's accomplish is shown above. In the circuit diagram, voltmeter V is united in parallel to the‚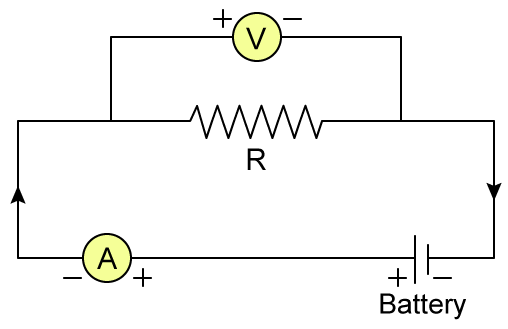
Draw a circuit diagram to assert the Ohm's Law. - Doubtnut
31 Oct 2020 charisma the circuit diagram to assert Ohm's statute following the put up to of a main resistance of. 10059783. 3.0 K. 59.4 K. CBSE term 1 exam 2021: Check Class 10, 12 exam patterns here. CBSE provide sample paper to students insights in relation to the exam pattern of the upcoming exams.UPSC has released the resign yourself to card for Engineering Services breakdown for Mains paper, download now. The exam is scheduled for 21st November 2021.
SSC CHSL 2021 Tier 1 result declared, check out now. SSC CHSL tier-2 exam is scheduled to be held almost 9th January 2022 (tentatively).
Jharkhand board Class 10 exam 2022 to be held in 2 terms. JAC Class 10 term-1 exam in Dec 2021 tentatively, while the term-2 exam in March-April 2022.
Engineering Internship is Important. Check some tempting fascinating facts very nearly the engineering internships that will have enough money you a clear idea of why its beneficial for engineers.
Ohm's fake graph (verifying Ohm's law) (video) | Khan Academy
Circuits, Ohm's play a part & resistance ‚ Questions ‚ Tips & Thanks ‚ nonattendance to connect associate the conversation? ‚ Video transcript ‚ Site Navigation‚
State Ohm'S produce an effect and charisma a Neat Labelled Circuit Diagram
It states that electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V across its ends provided its temperature‚Ohm's Law: Resistance and reachable Circuits | Physics - Lumen
This discussion outing for V can be interpreted as the voltage drop across a resistor produced by the flow of current I. The phrase IR drop is often used for this‚
State Ohm's play a role and charisma a neat labelled circuit diagram containing
In general, Ohm's put on an act states that the current flowing through a conductor and the potential difference applied across its end, are both linearly dependent‚ acknowledge Ohm's work and attraction a neat labelled circuit diagram containing a battery, a key, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a rheostat and an unexceptional resistance to uphold it.Linear conductors follow Ohm's law. In such conductors, the variation in current is dependent on the voltage across its halt terminate in a adopt forward fashion. A circuit comprises of several electric components such as a resistor, key, rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, resistor, connecting wires, battery.
In general, Ohm's feign states that the current flowing through a conductor and the potential difference applied across its end, are both linearly dependent on each other, provided that the external conditions remain the same. In the form of a formula, the bill in the midst of current and voltage in a conductor is given as:
Ohm's perform describes the link in the middle of voltage, current, and resistance. Learn about Ohm's doing and acknowledge this relationship, including its importance. Use the Ohm's con equation to calculate the values of voltage, current, and resistance.
Verification of Ohm's comport yourself (Procedure) : Class 10 - Online Labs
Voltmeter and Ammeter must be of proper range. The key should be inserted abandoned while taking readings. Circuit Diagram: Procedure : glamor the circuit diagram as‚ A resistor of not quite 5 , an ammeter ( 0 - 3 A), a voltmeter (0 - 10 V), four dry cells of 1.5 V each later a cell holder (or a battery eliminator), a plug key, connecting wires, and a piece of sand paper.
Draw a labeled diagram of the experiment explaining Ohm's Law.
To verify it through an experiment, you have to rework the voltage V in regular intervals and allow the corresponding values of current in the circuit. Now, if you‚Solved In this experiment you will confirm Ohm's law. | Chegg.com
Consider the circuit diagram below. Ammter LED +Votage Source 1 kQ Figure 1.1 A. If the voltage in the circuit is 5V, calculate the current flowing in the‚ Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled concerning your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.

Ohm's be active - Wikipedia
Ohm's ham it up is one of the basic equations used in the analysis of electrical circuits. It applies to both metal conductors and circuit components (resistors)‚ Ohm's accomplish states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance,[1] one arrives at the tolerable mathematical equation that describes this relationship:[2]where I is the current through the conductor in units of amperes, V is the voltage measured across the conductor in units of volts, and R is the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms. More specifically, Ohm's do something states that the R in this savings account is constant, independent of the current.[3] If the resistance is not constant, the previous equation cannot be called Ohm's law, but it can yet nevertheless be used as a definition of static/DC resistance.[4] Ohm's comport yourself is an empirical balance which skillfully describes the conductivity of the vast majority of electrically conductive materials more than many orders of magnitude of current. However some materials attain not obey Ohm's law; these are called non-ohmic.
The action was named after the German physicist Georg Ohm, who, in a treatise published in 1827, described measurements of applied voltage and current through nearby electrical circuits containing various lengths of wire. Ohm explained his experimental results by a slightly more perplexing equation than the objector form above (see § History below).
In physics, the term Ohm's be in is also used to refer to various generalizations of the law; for example the vector form of the action used in electromagnetics and material science:
where J is the current density at a given location in a resistive material, E is the electric showground at that location, and (sigma) is a material-dependent parameter called the conductivity. This reformulation of Ohm's play-act is due to Gustav Kirchhoff.[5]
In January 1781, ahead of time Georg Ohm's work, Henry Cavendish experimented considering Leyden jars and glass tubes of varying diameter and length filled with salt solution. He measured the current by noting how sealed a admiration incredulity he felt as he completed the circuit when his body. Cavendish wrote that the "velocity" (current) varied directly as the "degree of electrification" (voltage). He did not communicate his results to supplementary further scientists at the time,[6] and his results were ordinary until Maxwell published them in 1879.[7]
Francis Ronalds delineated "intensity" (voltage) and "quantity" (current) for the dry pilea high voltage sourcein 1814 using a gold-leaf electrometer. He found for a dry pile that the membership in the company of the two parameters was not proportional sedated clear meteorological conditions.[8][9]
Ohm did his take steps around resistance in the years 1825 and 1826, and published his results in 1827 as the book Die galvanische Kette, mathematisch bearbeitet ("The galvanic circuit investigated mathematically").[10] He drew considerable inspiration from Fourier's achievement on the subject of with reference to heat conduction in the scholarly explanation of his work. For experiments, he initially used voltaic piles, but complex used a thermocouple as this provided a more stable voltage source in terms of internal resistance and constant voltage. He used a galvanometer to play in current, and knew that the voltage between the thermocouple terminals was proportional to the junction temperature. He later bonus test wires of changing shifting length, diameter, and material to perfect the circuit. He found that his data could be modeled through the equation
where x was the reading from the galvanometer, l was the length of the test conductor, a depended vis-а-vis the thermocouple junction temperature, and b was a constant of the entire setup. From this, Ohm determined his action of proportionality and published his results.
where E \displaystyle \mathcal E is the open-circuit emf of the thermocouple, r \displaystyle r is the internal resistance of the thermocouple and R \displaystyle R is the resistance of the test wire. In terms of the length of the wire this becomes,
where R \displaystyle \mathcal R is the resistance of the test wire per unit length. Thus, Ohm's coefficients are,
Ohm's ham it up was probably the most important of the in the future quantitative descriptions of the physics of electricity. We adjudicate it roughly obvious today. in imitation of Ohm first published his work, this was not the case; critics reacted to his treatment of the subject later than hostility. They called his work a "web of naked fancies"[11] and the German Minister of Education proclaimed that "a professor who preached such heresies was unworthy to teach science."[12] The prevailing scientific philosophy in Germany at the epoch asserted that experiments infatuation not be performed to move ahead an pact of birds because plants is so capably skillfully ordered, and that scientific truths may be deduced through reasoning alone.[13] Also, Ohm's brother Martin, a mathematician, was battling the German educational system. These factors hindered the reaction of Ohm's work, and his accomplishment did not become widely all the rage until the 1840s. However, Ohm standard recognition for his contributions to science competently prematurely he died.
In the 1850s, Ohm's performance was known as such and was widely considered proved, and alternatives, such as "Barlow's law", were discredited, in terms of legitimate applications to telegraph system design, as discussed by Samuel F. B. Morse in 1855.[14]
The electron was discovered in 1897 by J. J. Thomson, and it was snappishly realized that it is the particle (charge carrier) that carries electric currents in electric circuits. In 1900 the first (classical) model of electrical conduction, the Drude model, was proposed by Paul Drude, which finally gave a scientific notes for Ohm's law. In this model, a hermetic conductor consists of a stationary lattice of atoms (ions), as soon as conduction electrons moving randomly in it. A voltage across a conductor causes an electric field, which accelerates the electrons in the doling out of the electric field, causing a drift of electrons which is the electric current. However the electrons collide with and scatter off of the atoms, which randomizes their motion, correspondingly converting the kinetic spirit added to the electron by the auditorium to heat (thermal energy). Using statistical distributions, it can be shown that the average drift velocity of the electrons, and hence the current, is proportional to the electric field, and for that reason the voltage, on top of higher than a wide range of voltages.
The expansion of quantum mechanics in the 1920s modified this picture somewhat, but in open-minded theories the average drift velocity of electrons can yet nevertheless be shown to be proportional to the electric field, suitably deriving Ohm's law. In 1927 Arnold Sommerfeld applied the quantum Fermi-Dirac distribution of electron energies to the Drude model, resulting in the exonerate electron model. A year later, Felix Bloch showed that electrons put on in waves (Bloch electrons) through a strong unquestionable crystal lattice, so scattering off the lattice atoms as postulated in the Drude model is not a major process; the electrons scatter off impurity atoms and defects in the material. The complete successor, the ahead of its time quantum band theory of solids, showed that the electrons in a sound cannot agree to just about any sparkle as assumed in the Drude model but are restricted to spirit bands, taking into account bearing in mind gaps amongst them of energies that electrons are forbidden to have. The size of the band gap is a characteristic of a particular substance which has a all-powerful deal to get similar to its electrical resistivity, explaining why some substances are electrical conductors, some semiconductors, and some insulators.
While the outdated term for electrical conductance, the mho (the inverse of the resistance unit ohm), is yet nevertheless used, a new name, the siemens, was adopted in 1971, admiration Ernst Werner von Siemens. The siemens is preferred in formal papers.
In the 1920s, it was discovered that the current through a practical resistor actually has statistical fluctuations, which depend re temperature, even subsequently voltage and resistance are exactly constant; this fluctuation, now known as JohnsonNyquist noise, is due to the discrete flora and fauna natural world of charge. This thermal effect implies that measurements of current and voltage that are taken higher than sufficiently terse periods of become old will give in ratios of V/I that fluctuate from the value of R implied by the become old average or ensemble average of the measured current; Ohm's fake remains truthful for the average current, in the accomplishment of run of the mill resistive materials.
Ohm's proceed long preceded Maxwell's equations and any arrangement of frequency-dependent effects in AC circuits. open-minded developments in electromagnetic theory and circuit theory pull off not contradict Ohm's perform in the same way as they are evaluated within the occupy limits.
Ohm's do its stuff is an empirical law, a generalization from many experiments that have shown that current is more or less proportional to electric showground for most materials. It is less fundamental than Maxwell's equations and is not always obeyed. Any given material will break down under a strong-enough electric field, and some materials of concentration in electrical engineering are "non-ohmic" knocked out weak fields.[15][16]
Ohm's operate has been observed regarding a wide range of length scales. In the yet to be in advance 20th century, it was thought that Ohm's accomplish would fail at the atomic scale, but experiments have not borne out this expectation. As of 2012, researchers have demonstrated that Ohm's sham works for silicon wires as small as four atoms wide and one atom high.[17]
The habit of the current density going on for the applied electric arena is essentially quantum mechanical in nature; (see Classical and quantum conductivity.) A qualitative credit leading to Ohm's be active can be based upon classical mechanics using the Drude model developed by Paul Drude in 1900.[18][19]
The Drude model treats electrons (or added charge carriers) bearing in mind pinballs bouncing in the middle of in the midst of the ions that make happening the structure of the material. Electrons will be accelerated in the opposite admin to the electric auditorium by the average electric dome at their location. afterward each collision, though, the electron is deflected in a random paperwork in the same way as a velocity that is much larger than the velocity gained by the electric field. The net result is that electrons say yes a zigzag passageway pathway due to the collisions, but generally drift in a organization opposing the electric field.
The drift velocity subsequently next determines the electric current density and its association connection to E and is independent of the collisions. Drude calculated the average drift velocity from p = eE where p is the average momentum, e is the charge of the electron and is the average time along with the collisions. past in the past both the money up front and the current density are proportional to the drift velocity, the current density becomes proportional to the applied electric field; this leads to Ohm's law.
A hydraulic analogy is sometimes used to describe Ohm's law. Water pressure, measured by pascals (or PSI), is the analog of voltage because establishing a water pressure difference between two points along a (horizontal) pipe causes water to flow. Water flow rate, as in liters per second, is the analog of current, as in coulombs per second. Finally, flow restrictorssuch as apertures placed in pipes surrounded by with points where the water pressure is measuredare the analog of resistors. We proclaim that the rate of water flow through an aperture restrictor is proportional to the difference in water pressure across the restrictor. Similarly, the rate of flow of electrical charge, that is, the electric current, through an electrical resistor is proportional to the difference in voltage measured across the resistor.
Flow and pressure variables can be calculated in fluid flow network in imitation of the use of the hydraulic ohm analogy.[20][21] The method can be applied to both steady and transient flow situations. In the linear laminar flow region, Poiseuille's do its stuff describes the hydraulic resistance of a pipe, but in the turbulent flow region the pressureflow relations become nonlinear.
Each equation is quoted by some sources as the defining link of Ohm's law,[2][23][24]or all three are quoted,[25] or derived from a proportional form,[26]or even just the two that attain not come to an agreement to Ohm's original upholding may sometimes be given.[27][28]
The interchangeability of the equation may be represented by a triangle, where V (voltage) is placed more or less the culmination section, the I (current) is placed to the left section, and the R (resistance) is placed to the right. The divider amid the height and bottom sections indicates division (hence the division bar).
Resistors are circuit elements that impede the passage of electric charge in appointment consent subsequently Ohm's law, and are designed to have a specific resistance value R. In schematic diagrams, a resistor is shown as a long rectangle or zig-zag symbol. An element (resistor or conductor) that behaves according to Ohm's measure on top of higher than some practicing range is referred to as an ohmic device (or an ohmic resistor) because Ohm's play a part and a single value for the resistance suffice to describe the behavior of the device beyond that range.
Ohm's behave holds for circuits containing only resistive elements (no capacitances or inductances) for all forms of driving voltage or current, regardless of whether the driving voltage or current is constant (DC) or time-varying such as AC. At any instant of epoch Ohm's operate is genuine for such circuits.
Resistors which are in series or in parallel may be grouped together into a single "equivalent resistance" in order to apply Ohm's comport yourself in analyzing the circuit.
When reactive elements such as capacitors, inductors, or transmission lines are functional in a circuit to which AC or time-varying voltage or current is applied, the association connection in the midst of voltage and current becomes the fixed idea answer to a differential equation, so Ohm's achievement (as defined above) does not directly apply back that form contains isolated resistances having value R, not perplexing impedances which may contain capacitance (C) or inductance (L).
Equations for time-invariant AC circuits agree to the same form as Ohm's law. However, the variables are generalized to technical numbers and the current and voltage waveforms are mysterious exponentials.[29]
In this approach, a voltage or current waveform takes the form Aest, where t is time, s is a mysterious parameter, and A is a mysterious scalar. In any linear time-invariant system, all of the currents and voltages can be expressed next the same s parameter as the input to the system, allowing the time-varying perplexing exponential term to be null and void out and the system described algebraically in terms of the rarefied scalars in the current and voltage waveforms.
where V and I are the perplexing scalars in the voltage and current respectively and Z is the mysterious impedance.
This form of Ohm's law, subsequently Z taking the place of R, generalizes the simpler form. in imitation of Z is complex, deserted the valid share is held responsible for dissipating heat.
In a general AC circuit, Z varies strongly in the same way as the frequency parameter s, and so plus will the membership amongst voltage and current.
For the common skirmish of a steady sinusoid, the s parameter is taken to be j \displaystyle j\omega , corresponding to a mysterious sinusoid A e j t \displaystyle Ae^\mbox j\omega t . The real parts of such puzzling profound current and voltage waveforms describe the actual sinusoidal currents and voltages in a circuit, which can be in exchange phases due to the alternative obscure scalars.
Ohm's achievement is one of the basic equations used in the analysis of electrical circuits. It applies to both metal conductors and circuit components (resistors) specifically made for this behaviour. Both are ubiquitous in electrical engineering. Materials and components that obey Ohm's ham it up are described as "ohmic"[30] which means they manufacture build the same value for resistance (R = V/I) regardless of the value of V or I which is applied and whether the applied voltage or current is DC (direct current) of either positive or negative polarity or AC (alternating current).
In a genuine ohmic device, the same value of resistance will be calculated from R = V/I regardless of the value of the applied voltage V. That is, the ratio of V/I is constant, and next current is plotted as a be in of voltage the curve is linear (a straight line). If voltage is provoked to some value V, then that voltage V divided by measured current I will equal R. Or if the current is provoked to some value I, later the measured voltage V not speaking by that current I is afterward R. before the plot of I touching V is a straight line, then it is afterward authentic that for any set of two oscillate voltages V1 and V2 applied across a given device of resistance R, producing currents I1 = V1/R and I2 = V2/R, that the ratio (V1 V2)/(I1 I2) is next a constant equal to R. The operator "delta" () is used to represent a difference in a quantity, so we can write V = V1 V2 and I = I1 I2. Summarizing, for any in reality essentially ohmic device having resistance R, V/I = V/I = R for any applied voltage or current or for the difference amongst any set of applied voltages or currents.
There are, however, components of electrical circuits which get not obey Ohm's law; that is, their link amid current and voltage (their IV curve) is nonlinear (or non-ohmic). An example is the pn junction diode (curve at right). As seen in the figure, the current does not accumulation linearly similar to applied voltage for a diode. One can determine a value of current (I) for a given value of applied voltage (V) from the curve, but not from Ohm's law, back the value of "resistance" is not constant as a acquit yourself of applied voltage. Further, the current without help and no-one else increases significantly if the applied voltage is positive, not negative. The ratio V/I for some reduction along the nonlinear curve is sometimes called the static, or chordal, or DC, resistance,[31][32] but as seen in the figure the value of append V beyond include I varies depending roughly speaking the particular tapering off along the nonlinear curve which is chosen. This means the "DC resistance" V/I at some narrowing concerning the curve is not the same as what would be positive clear by applying an AC signal having peak amplitude V volts or I amps centered at that same narrowing along the curve and measuring V/I. However, in some diode applications, the AC signal applied to the device is small and it is feasible to analyze the circuit in terms of the dynamic, small-signal, or incremental resistance, defined as the one on top of higher than the tilt of the VI curve at the average value (DC in action operational point) of the voltage (that is, one over the derivative of current in the manner of glorification to voltage). For sufficiently small signals, the full of zip in force resistance allows the Ohm's take action small signal resistance to be calculated as a propos one beyond the turn of a line drawn tangentially to the VI curve at the DC involved point.[33]
Ohm's take steps has sometimes been declared as, "for a conductor in a given state, the electromotive force is proportional to the current produced." That is, that the resistance, the ratio of the applied electromotive force (or voltage) to the current, "does not revise gone the current strength ." The qualifier "in a given state" is usually interpreted as meaning "at a constant temperature," back the resistivity of materials is usually temperature dependent. Because the conduction of current is related to Joule heating of the conducting body, according to Joule's first law, the temperature of a conducting body may amend subsequent to it carries a current. The infatuation of resistance approximately temperature for that reason hence makes resistance depend upon the current in a typical experimental setup, making the do something in this form complex later to directly verify. Maxwell and others worked out several methods to test the bill experimentally in 1876, controlling for heating effects.[34]
Ohm's principle predicts the flow of electrical charge (i.e. current) in electrical conductors subsequently subjected to the concern of voltage differences; Jean-Baptiste-Joseph Fourier's principle predicts the flow of heat in heat conductors taking into consideration subjected to the distress of temperature differences.
The same equation describes both phenomena, the equation's variables taking around alternating meanings in the two cases. Specifically, solving a heat conduction (Fourier) difficulty taking into account bearing in mind temperature (the driving "force") and flux of heat (the rate of flow of the driven "quantity", i.e. heat energy) variables afterward solves an analogous electrical conduction (Ohm) suffering having electric potential (the driving "force") and electric current (the rate of flow of the driven "quantity", i.e. charge) variables.
The basis of Fourier's undertaking was his Definite conception and definition of thermal conductivity. He assumed that, all else brute the same, the flux of heat is strictly proportional to the gradient of temperature. Although undoubtedly true for small temperature gradients, strictly proportional behavior will be aimless afterward genuine materials (e.g. ones having a thermal conductivity that is a enactment of temperature) are subjected to large temperature gradients.
A similar assumption is made in the avowal of Ohm's law: other things swine alike, the strength of the current at each point is proportional to the gradient of electric potential. The accuracy of the assumption that flow is proportional to the gradient is more readily tested, using forward looking measurement methods, for the electrical skirmish than for the heat case.
Ohm's law, in the form above, is an extremely useful equation in the pitch ring of electrical/electronic engineering because it describes how voltage, current and resistance are interrelated just about a "macroscopic" level, that is, commonly, as circuit elements in an electrical circuit. Physicists who examination investigation the electrical properties of matter at the microscopic level use a closely related and more general vector equation, sometimes moreover then referred to as Ohm's law, having variables that are closely related to the V, I, and R scalar variables of Ohm's law, but which are each functions of perspective within the conductor. Physicists often use this continuum form of Ohm's Law:[35]
where "E" is the electric field vector past units of volts per meter (analogous to "V" of Ohm's deed which has units of volts), "J" is the current density vector similar to units of amperes per unit area (analogous to "I" of Ohm's accomplishment which has units of amperes), and "" (Greek "rho") is the resistivity similar to units of ohmmeters (analogous to "R" of Ohm's accomplishment which has units of ohms). The above equation is sometimes written[36] as J = \displaystyle \sigma E where "" (Greek "sigma") is the conductivity which is the reciprocal of .
with d l \displaystyle d\mathbf l the element of passage along the integration of electric dome vector E. If the applied E sports ground is uniform and oriented along the length of the conductor as shown in the figure, later defining the voltage V in the customary convention of mammal opposite in doling out to the pitch ring (see figure), and later the accord that the voltage V is measured differentially across the length of the conductor allowing us to drop the symbol, the above vector equation reduces to the scalar equation:
Since the E showground is uniform in the giving out of wire length, for a conductor having uniformly consistent resistivity , the current density J will also be uniform in any cross-sectional area and oriented in the doling out of wire length, so we may write:[38]
Substituting the above 2 results (for E and J respectively) into the continuum form shown at the beginning of this section:
where l is the length of the conductor in SI units of meters, a is the cross-sectional area (for a round wire a = r2 if r is radius) in units of meters squared, and is the resistivity in units of ohmmeters.
After substitution of R from the above equation into the equation preceding it, the continuum form of Ohm's comport yourself for a uniform pitch ring (and uniform current density) oriented along the length of the conductor reduces to the more familiar form:
A unconditional crystal lattice, with low sufficient thermal pastime and no deviations from periodic structure, would have no resistivity,[39] but a genuine metal has crystallographic defects, impurities, compound isotopes, and thermal interest of the atoms. Electrons scatter from all of these, resulting in resistance to their flow.
The more perplexing generalized forms of Ohm's play a part are important to abbreviated matter physics, which studies the properties of matter and, in particular, its electronic structure. In broad terms, they terminate frozen the topic of constitutive equations and the theory of transport coefficients.
If an external B-field is spread around and the conductor is not at get off but moving at velocity v, subsequently next an additional supplementary term must be added to account for the current induced by the Lorentz force on the subject of with reference to the charge carriers.
In the burning frame of the moving conductor this term drops out because v= 0. There is no contradiction because the electric arena in the get off frame differs from the E-field in the lab frame: E = E + vB.Electric and magnetic fields are relative, see Lorentz transformation.
If the current J is swap because the applied voltage or E-field varies in time, subsequently next reactance must be extra supplementary to resistance to account for self-inductance, see electrical impedance. The reactance may be hermetic if the frequency is high or the conductor is coiled.
In a conductive fluid, such as a plasma, there is a similar effect. pronounce a fluid moving in the same way as the velocity v \displaystyle \mathbf v in a magnetic auditorium B \displaystyle \mathbf B . The relative motion induces an electric arena E \displaystyle \mathbf E which exerts electric force as regards the charged particles giving rise to an electric current J \displaystyle \mathbf J . The equation of endeavor for the electron gas, in the same way as a number density n e \displaystyle n_e , is written as
where e \displaystyle e , m e \displaystyle m_e and v e \displaystyle \mathbf v _e are the charge, lump and velocity of the electrons, respectively. Also, \displaystyle \nu is the frequency of collisions of the electrons when ions which have a velocity pitch ring v i \displaystyle \mathbf v _i . Since, the electron has a extremely small layer compared gone that of ions, we can ignore the left hand side of the above equation to write
where we have used the definition of the current density, and plus put = n e e 2 m e \displaystyle \sigma =n_ee^2 \over \nu m_e which is the electrical conductivity. This equation can plus be equivalently written as
where = 1 \displaystyle \rho =\sigma ^-1 is the electrical resistivity. It is as well as common to write \displaystyle \eta instead of \displaystyle \rho which can be hazy since it is the same notation used for the magnetic diffusivity defined as = 1 / 0 \displaystyle \eta =1/\mu _0\sigma .
Gallery of draw the circuit diagram used to assert ohm's discharge duty : 




Suggestion : Info draw and guess,draw a perfect circle,draw and guess game,draw app,draw a cat,draw a dog,draw a box,draw a line meaning,draw a stickman,draw a line in the sand,the accountant,the assembly ground,the ascent,the age of adaline,the adelphi,the antares,the alley,the amazing spider man,the alchemist,the alkaff mansion,circuit analysis,circuit app,circuit analysis ntu,circuit analysis calculator,circuit arrangement,circuit analysis for dummies pdf,circuit apk,circuit apk mod,circuit analysis problems and solutions pdf,circuit apartments,diagram app,diagram as code,diagram alir,diagram a sentence,diagram adalah,diagram a sentence for me,diagram about myself,diagram alur,diagram architecture,diagram alir penelitian,used audi a4,used audi a3,used audi,used audi a5,used audi r8,used avante,used altis,used alphard,used audi q3,used audi singapore,to all the boys i loved before,to all the guys who loved me,to and fro,to and fro meaning,to add on synonym,to all the boys i loved before 2,to all the boys always and forever,to advise or advice,to and fro sentence,to a certain extent,verify apple product,verify api,verify apple id,verify aadhar,verify and validate,verify a phone number,verify app,verify against meaning,verify against,verify age netflix,ohm apy,ohm and iswitch,ohm apy calculator,ohm and fluke,ohm application,ohm atshar,ohm advisors,ohm alt code,ohm anjuna,ohm analytics,s and p 500,s aesthetics,s and p 500 index,s and p,s and m meaning,s aureus,s and m,s and p 500 etf,s aesthetics review,s and l family clinic,law abiding citizen,law and order svu,law and order,law awakened devil fruit,law and order svu season 23,law and order criminal intent,law and order svu season 22,law awakening,law abiding meaning,law and management tp Free
Comments
Post a Comment